
ంభం. మా వినియోగదారుల నమ్మకానికి ఎప్పుడూ ద్రోహం చేయకూడదనే మా నిబద్ధతను మేము నిలకడగా సమర్థించాము, మా వ్యవహారాలన్నింటిలోనూ పారదర్శకత మరియు నిజాయితీని నిర్ధారిస్తాము. అదనంగా, నాణ్యతకు ఎల్లప్పుడూ పరిమాణంపై ప్రాధాన్యత ఇవ్వబడుతుంది, అసాధారణమైన ప్రమాణాలు మరియు కస్టమర్ సంతృప్తికి హామీ ఇవ్వడానికి ఉత్పత్తి ప్రక్రియ యొక్క ప్రతి దశలో కఠినమైన నాణ్యత నియంత్రణ చర్యలు అమలు చేయబడతాయి.
మా బృందం
ఇది మార్కెట్లో నిలబడటానికి మరియు విస్తృత కస్టమర్ల స్థావరాన్ని సేకరించడానికి వీలు కల్పించిన మా జట్టు సభ్యుల వెనుక భాగం. అర్హత, అనుభవం, నైపుణ్యాలు మరియు జ్ఞానం ఆధారంగా, మేము మా జట్టు సభ్యులకు ఒక జట్టు మరియు నిర్దిష్ట హోదాను కేటాయించాము. మేము పరిపూర్ణతతో ప్రతి పనికి మమ్మల్ని ఎనేబుల్ మరియు కస్టమర్ల అంచనాలను మించిపోయే మా జట్టు సభ్యుల గురించి గర్వపడుతున్నాము. మేము మా ఉద్యోగులకు అవసరమైన శిక్షణా కార్యక్రమాలను కూడా అందిస్తాము, తద్వారా వారి నైపుణ్యాలను మెరుగుపరచవచ్చు మరియు వారు సంబంధిత డొమైన్లో ముందుకు ఉండగలరు.
మాకు ఎందుకు?
- మేము ఉత్తమ ముడి పదార్థం మరియు తాజా ఉత్పత్తి సాంకేతిక ఉపయోగించి వాటిని తయారీదారు మా ఉత్పత్తుల ప్రీమియం నాణ్యత హామీ.
- కొనుగోలుదారు యొక్క అంచనాలను మరియు వ్యాపార మా స్వభావాన్ని దృష్టిలో ఉంచుకుని రూపొందించబడిన సరసమైన విధానాలను మేము అభ్యసిస్తాము.
- మేము ఫిల్మ్ డ్రైయర్, మురుగునీటి ఆవిరైటర్లు, మెంబ్రేన్ బయోరియాక్టర్, లిక్విడ్ డిశ్చార్జ్ సిస్టమ్, లిక్విడ్ డిశ్చార్జ్ సిస్టమ్ మొదలైన వాటితో సహా మా ఉత్పత్తులకు సరసమైన ధరను వసూలు చేస్తాము, తద్వారా వినియోగదారులు ఆర్థికంగా దోపిడీకి గురవుతున్నారని
కేటగిరీలు
- బాష్పీభవన మొక్కలు
- మల్టిపుల్ ఎఫెక్ట్ ఆవిరిపోరేటర్లు
- మురుగునీటి ఆవిరిపోరేటర్లు
- కదిలిన సన్నని ఫిల్మ్ డ్రైయర్
- సున్నా ద్రవ ఉత్సర్గ వ్యవస్థ
- ఫోర్స్డ్ సర్క్యులేషన్ ఆవిరిపోరేటర్
- మెంబ్రేన్ బయోఇయాక్టర్
- పారిశ్రామిక ఆవిరిపోరేటర్లు
- Wastewater Treatment Plants
- Wastewater Treatment Plants
- Wastewater Treatment Plants
- Industrial Evaporators
- Industrial Evaporators
- Industrial Evaporators
- Wastewater Treatment Plants
- Industrial Dryers
- Industrial Dryers
- Industrial Evaporators
- Industrial Evaporators
- Industrial Evaporators
About Us

Agitated thin film dryer
వస్తువు యొక్క వివరాలు:
- ఉత్పత్తి రకం Agitated Thin Film Dryer
- ఎత్తు మీటర్ (m)
- పొడవు మీటర్ (m)
- బరువు కిలోగ్రాములు (కిలోలు)
- వెడల్పు మీటర్ (m)
- ఒత్తిడి బార్
- వాడుక Industrial
- మరింత వీక్షించడానికి క్లిక్ చేయండి
ధర మరియు పరిమాణం
- 1
ఉత్పత్తి లక్షణాలు
- మీటర్ (m)
- కిలోగ్రాములు (కిలోలు)
- మీటర్ (m)
- మీటర్ (m)
- బార్
- Industrial
- Agitated Thin Film Dryer
- Yes
వాణిజ్య సమాచారం
- నెలకు
- డేస్
- Wooden
ఉత్పత్తి వివరణ
What is an Agitated Thin Film Dryer (ATFD)?
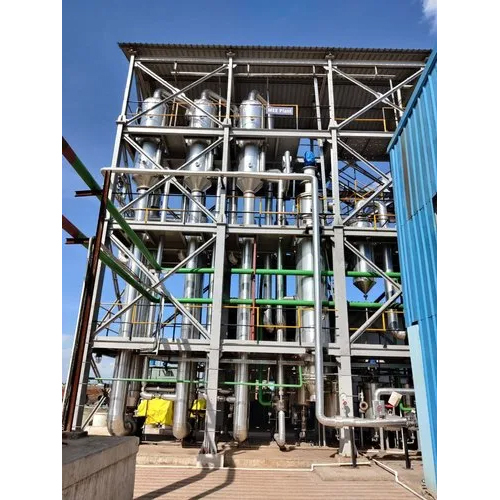
An Agitated Thin Film Dryer (ATFD) is a type of evaporator that dries highly viscous and heat-sensitive materials by spreading them into a thin film and agitating them on a heated surface. This method ensures efficient heat transfer and rapid evaporation of solvents or moisture, leaving behind a dry product. Various industries, such as chemical, pharmaceutical, food, and wastewater treatment, rely on ATFDs due to their ability to handle challenging drying processes with high efficiency and minimal thermal degradation.
Key Components of ATFD
Before diving into the working principle, it is essential to understand the key components of an ATFD:
- Feed System: Introduces the liquid, slurry, or paste to the drying process.
- Rotating Shaft with Blades or Wipers: Agitates the material, ensuring it forms a thin, even film on the heated surface.
- Heated Surface (Jacketed Cylinder): Provides the necessary heat for evaporation.
- Vapor Outlet: Removes the evaporated moisture or solvent.
- Discharge System: Collects the dried product.
Working Principle of ATFD
The ATFD operates on a relatively straightforward yet highly effective principle. Here is a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
1. Feed Introduction
The feed system introduces the wet material into the ATFD. This material can be a liquid, slurry, or paste, depending on the application. Operators carefully control the feed rate to ensure consistent drying.
2. Formation of Thin Film
Once the material enters the dryer, it encounters the rotating shaft equipped with blades or wipers. These blades spread the material into a thin film across the inner surface of the heated cylinder. The thin film formation maximizes the surface area for heat transfer, facilitating rapid evaporation.
3. Agitation
The rotating blades continuously agitate the thin film, preventing it from adhering to the heated surface and promoting uniform drying. This agitation also helps break down any potential crust that may form on the surface, ensuring the entire material is evenly exposed to the heat.
4. Heat Transfer and Evaporation
The jacketed cylinder is heated using steam, hot water, or thermal oil. The heat transfers through the cylinder wall to the thin film of the material. Due to the large surface area and thin film, the moisture or solvent evaporates quickly. The vapor generated during this process exits through the vapor outlet.
5. Discharge of Dried Product
As the material moves along the heated surface, it loses its moisture content and transitions into a dry powder or granules. The blades continuously scrape off the dried product, discharging it through the bottom of the ATFD.
Advantages of ATFD
ATFDs offer several advantages that make them an ideal choice for drying challenging materials:
High Efficiency
The thin film and continuous agitation ensure efficient heat transfer and rapid evaporation, leading to high drying rates and energy savings.
Uniform Drying
Constant agitation prevents the formation of hot spots and ensures uniform drying of the material.
Handling Heat-Sensitive Materials
ATFDs can operate at low temperatures, making them suitable for drying heat-sensitive materials without causing thermal degradation.
Scalability
ATFDs are available in various sizes, making them suitable for small-scale laboratory applications and large-scale industrial processes.
Low Residence Time
The short residence time of the material in the ATFD minimizes the risk of degradation or chemical changes, preserving the quality of the dried product.

Price: Â
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Vacuum Evaporator లో ఇతర ఉత్పత్తులు



















 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese